Cosmetic dentistry grafts and dental implants play vital roles in dental restoration. If you’re dealing with tooth loss or gum issues, these procedures might be the solution you’re looking for. This article will explain what these treatments involve and their benefits.
Key Takeaways
Cosmetic dentistry grafts are essential for successful dental implants, providing a strong foundation by addressing bone deficiencies.
Different types of bone grafts, including autografts, allografts, xenografts, and synthetic grafts, offer various benefits and applications for dental restoration.
Combining bone grafts with dental implants enhances stability, improves facial aesthetics, and supports long-term oral health by maintaining bone density.
Understanding Cosmetic Dentistry Grafts
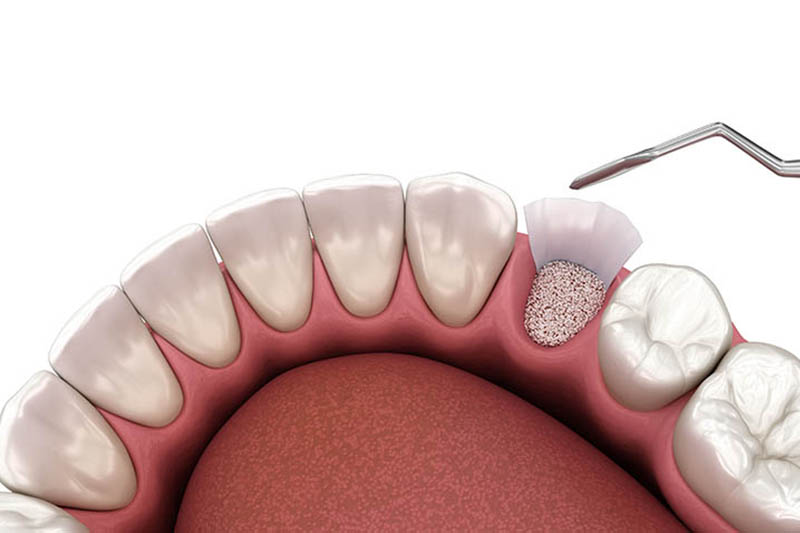
In cosmetic dentistry, bone grafts play an essential role in numerous dental restoration processes, with a particular emphasis on implant placement. A bone graft for this purpose aims to augment the quantity of natural bone within a portion of the jawbone where it may be lacking. This step is vital because a robust amount of natural bone is necessary to ensure both successful implant placement and its long-term stability.
The need for bone grafting emerges when there is insufficient natural bone available to anchor an implant securely. The shortage could be due to various causes, such as tooth loss, gum disease, or even the gradual resorption that naturally occurs over time following tooth loss. To perform a graft, materials can be sourced from several places: they might come from another area within one’s own body (autograft), donated tissue (allograft), or synthetic substitutes designed specifically for this use (alloplast). Anyone contemplating dental restorations must grasp how critical understanding bone grafting procedures are. These methods correct underlying deficiencies crucial for ensuring that subsequent placements of dental implants will succeed.
Ultimately, through proper dental bone grafting techniques, practitioners create an enduring foundation where implants are placed solidly—mimicking similar support functions provided by natural tooth roots—capable of durable performance akin to real teeth. Dental implant success enhances their anchorage and contributes positively toward maintaining facial structure health and aesthetics while safeguarding health and alignment among neighboring teeth.
Types of Bone Grafts Used in Cosmetic Dentistry
In cosmetic dentistry, various bone grafts are employed for their distinct advantages and specific uses. Options such as autografts, allografts, xenografts, and synthetic alternatives exist to cater to different needs. Comprehending these diverse choices is vital when deciding the most suitable method for securing dental implants.
Autografts for Cosmetic Dentistry
Bone grafting with autografts is considered the premier choice, offering unparalleled effectiveness. This technique utilizes bone taken from the patient’s own body, frequently sourced from either the jaw or hip, to restore a deficient area. Employing one’s own bone diminishes infection risks and boasts a high rate of success when used in dental implant procedures.
This approach typically necessitates an extended recuperation period due to the extra surgical site required to extract the graft material. Even so, due to their superior compatibility and efficacy in anchoring dental implants firmly within the jawbone structure, many patients and aesthetic dentists continue to favor autografts despite these considerations.
Allografts in Cosmetic Procedures
Bone allografts incorporate tissue from a deceased human donor, commonly obtained from cadaver bone. They offer a readily accessible and economical option that is less complex than the use of autografts. To guarantee the safety of recipients, this donated bone undergoes meticulous processing, sterilization, and screening for any infectious diseases.
Despite the high success rate associated with allografts, there are inherent risks, such as possible rejection or infection following the procedure. Adherence to stringent protocols established by the American Association of Tissue Banks (AATB) helps significantly reduce these concerns.
Xenografts for Aesthetic Improvements
In cosmetic dentistry, xenografts, which are typically sourced from bovine animals due to their congruence with human bone, are preferred for their ready availability and efficiency in promoting the regeneration of bone surrounding dental implants.
Synthetic Bone Grafts in Cosmetic Dentistry
Synthetic bone grafts use man-made materials, such as hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, and bioactive glass, to facilitate bone regeneration and promote the rapid growth of new bone.
These artificial grafts are a particularly valuable alternative for individuals who prefer not to or are unable to utilize natural donor bone for grafting purposes.
The Role of Bone Grafting in Dental Implants
Bone grafting is an essential step in ensuring the success of dental implants. A bone graft becomes necessary to rebuild jawbone structure when there’s not enough natural bone present, typically due to tooth loss or gum disease.
By bolstering implant integration and enhancing surrounding bone support, these grafts significantly reduce implant failure risks while boosting stability for enduring results.
Another crucial benefit provided by bone grafts is preserving overall jaw health by maintaining appropriate bone density and avoiding resorption. This preservation ensures the oral structures remain intact for the effective long-term functioning of any dental restorations placed.
In summary, bone grafting is instrumental in successful dentistry interventions by supporting secure implant placement and promoting durable outcomes from dental implant procedures.
The Bone Grafting Procedure for Dental Implants
Bone grafting in preparation for dental implants involves multiple stages, starting with the first consultation and continuing through aftercare, ensuring that patients are ready for an efficient dental implant procedure.
Initial Consultation and Evaluation
The initial phase of the bone grafting process involves an in-depth consultation and assessment, which includes examining your medical history and utilizing X-rays or CT scans. This preliminary step is crucial for devising a strategic plan for the procedure to ensure optimal results.